How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone components, essential flight techniques, and best practices for capturing stunning visuals.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will empower you to take to the skies with confidence.
Understanding your drone’s capabilities and limitations is paramount. This involves familiarizing yourself with its various components, from the propellers and motors that provide lift and movement to the sophisticated flight controller, GPS system, and camera that enable precise navigation and high-quality image capture. We’ll delve into each component’s function, ensuring you have a solid understanding of how your drone works before you even think about taking off.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. This section details the function of each major component and their interplay.
Major Drone Components
A typical drone comprises several key components working in concert. These include propellers, motors, a flight controller, a battery, a GPS module, and a camera.
| Component | Function | Component | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust, enabling flight and maneuverability. | Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, processing data from various sensors and controlling motor speeds to maintain stability and execute commands. |
| Motors | Spin the propellers, providing the necessary power for flight. | Battery | Provides power to all drone components. Flight time is directly related to battery capacity and usage. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data, enabling features like GPS-assisted flight and Return-to-Home (RTH) functionality. | Camera | Captures images and videos, offering various settings for adjusting image quality. |
Transmitter and Receiver
The transmitter and receiver are essential for controlling the drone. The transmitter, held by the pilot, sends commands wirelessly to the drone’s receiver. The receiver interprets these signals and relays them to the flight controller, allowing the pilot to control the drone’s movements.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful flight. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, always perform the following checks:
- Check battery level and ensure it’s sufficiently charged.
- Verify a strong GPS signal; weak signals can impair flight stability and RTH functionality.
- Inspect propellers for damage; bent or cracked propellers can cause instability or failure.
- Ensure all components are securely fastened and functioning correctly.
- Check for any obstructions in the immediate flight area.
Compass and IMU Calibration

Calibrating the drone’s compass and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) before each flight is essential for accurate flight control. The compass provides directional information, while the IMU measures the drone’s orientation and movement. Improper calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior.
Pre-Flight Safety Inspection
A comprehensive visual inspection of the drone is critical. Check for any loose parts, damaged components, or signs of wear and tear. Pay close attention to the propellers, motors, and the overall structural integrity of the drone.
Taking Off and Landing

Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. Mastering these techniques minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures the longevity of your drone.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
A smooth and controlled takeoff involves several steps. Begin by powering on the transmitter, followed by the drone. Wait for the GPS signal to lock and confirm a stable connection. Gently increase throttle to lift off vertically, maintaining a steady ascent rate.
Landing Techniques
There are different landing techniques to consider, depending on the situation. A normal landing involves a slow, controlled descent to the ground. An emergency landing might be necessary if there’s a malfunction or unexpected event, requiring a quick and safe descent to minimize damage.
Handling Unexpected Situations, How to operate a drone
Unexpected situations can occur, such as loss of signal or low battery warnings. In such cases, initiate an immediate emergency landing procedure. Familiarize yourself with your drone’s RTH functionality, a crucial safety feature.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the drone’s control sticks and their functions is essential for executing basic maneuvers. Practice is key to mastering these skills.
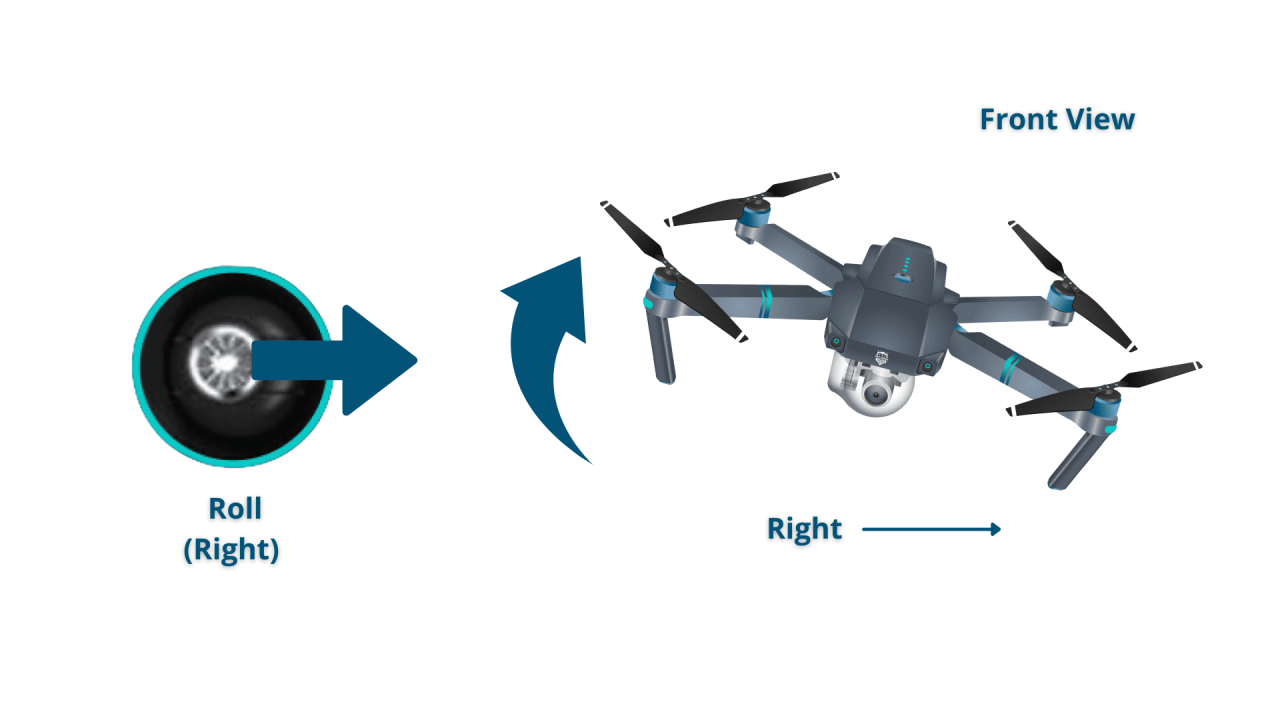
Control Stick Functions
Most drones use two control sticks: one for throttle and pitch/roll, and the other for yaw. The throttle controls altitude, while pitch and roll control forward/backward and side-to-side movement. Yaw controls rotation around the drone’s vertical axis.
Basic Maneuvers
Hovering involves maintaining a steady position in the air. Moving forward/backward and side-to-side requires controlled adjustments to the pitch and roll sticks. Turning involves using the yaw stick to rotate the drone.
Navigating Obstacles
Navigating obstacles requires careful control of the drone’s movement. Use smooth, deliberate movements to avoid collisions. Maintain a safe distance from obstacles, and always be aware of your surroundings.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques enable more complex and creative drone operations. These require a solid understanding of basic flight controls and a willingness to practice.
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Flight Modes
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path, with the drone autonomously following the defined points. Automated flight modes, such as altitude hold and GPS mode, simplify complex maneuvers and enhance stability.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Altitude hold maintains a consistent altitude, while GPS mode utilizes GPS data for precise positioning. Attitude mode provides more responsive control but requires more skill.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety protocols and regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently and safely operate your drone.
Proper training is essential before attempting any flight.
Flight Plan Example
A sample flight plan might involve taking off, orbiting a subject at a specific altitude and distance, then following a pre-programmed path, before returning to the starting point. This requires careful planning and execution using waypoint navigation and automated flight modes.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The drone’s camera is a key feature, offering the ability to capture stunning aerial photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and techniques is crucial for high-quality image capture.
Camera Settings
Typical drone camera settings include shutter speed, ISO, and aperture. Shutter speed controls motion blur, ISO affects image brightness and noise, and aperture controls depth of field.
Image Stabilization
Image stabilization technology minimizes the effects of vibrations and movement, resulting in sharper, clearer images and videos. This is particularly important during flight, where vibrations can significantly impact image quality.
Tips for High-Quality Capture
Consider these key aspects for capturing professional-quality aerial photos and videos: proper lighting, optimal camera settings for the scene, stable flight, and careful composition. Experiment with different settings and angles to achieve your desired results.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount. Understanding potential hazards and adhering to regulations is crucial for preventing accidents and legal issues.
Potential Hazards
Potential hazards include collisions with obstacles or people, battery failure leading to uncontrolled descent, loss of signal resulting in loss of control, and damage to the drone itself.
Safety Precautions
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Check weather conditions before flying.
- Never fly near people or property without permission.
- Always have a backup plan in case of emergencies.
Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Research and comply with all local, state, and federal laws concerning drone operation, including registration requirements and airspace restrictions. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal penalties.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: How To Operate A Drone
Despite careful preparation, problems can occur. Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues can minimize downtime and ensure continued safe operation.
Common Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Initiate an immediate landing procedure. Charge the battery fully before the next flight. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception. Ensure the GPS module is functioning correctly. |
| Motor Malfunction | Inspect the motor for damage. If necessary, seek professional repair. |
Camera and Image Transmission Issues
Problems with the camera or image transmission can often be resolved by checking the camera settings, ensuring a strong connection between the drone and controller, and restarting the drone.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
In case of a crash, carefully assess the damage. Repair minor issues yourself, but seek professional help for more extensive damage. Always prioritize safety when handling a damaged drone.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure its continued reliable performance.
Maintenance Schedule
Develop a regular maintenance schedule, including visual inspections for damage, cleaning the drone and propellers, and checking the battery health. Frequency depends on usage, but regular checks are recommended.
Proper Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep the battery charged to around 50% to prolong its lifespan. Store all accessories in a designated case or container to prevent damage or loss.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and understanding of the controls; for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation is a combination of knowledge and hands-on experience.
Identifying Wear and Tear
Regularly inspect the drone for signs of wear and tear, such as cracks in the frame, loose screws, or damaged propellers. If you notice significant damage, seek professional repair to avoid further problems.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, focusing on safety protocols, and consistently practicing your skills, you’ll be well-equipped to explore the exciting world of aerial flight. Remember, responsible operation is key; always prioritize safety and adhere to local regulations. With dedication and the right knowledge, you’ll soon be capturing stunning aerial footage and enjoying the thrill of flight from a unique perspective.
Helpful Answers
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are suitable for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time on a single charge.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a “return-to-home” function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
How do I clean my drone?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe down the drone body. Avoid using harsh chemicals or water.